Lignin
We search for new, more valuable application areas for lignin, for example nanoparticles or coatings.
Lignin is the second most abundant natural raw material and nature’s most abundant aromatic polymer, which can be found in plants. Lignin is generally obtained from black liquor as a waste from pulp industry in large quantities. Although much of the lignin produced by pulp industry is currently consumed as a fuel, there are other, higher value added applications, such as carbon material precursor, emulsifier, coating, filler or substitute for metal/inorganic nanoparticles. We study these new areas for lignin utilization, envisioning lignin’s transition from waste into a valuable raw material.
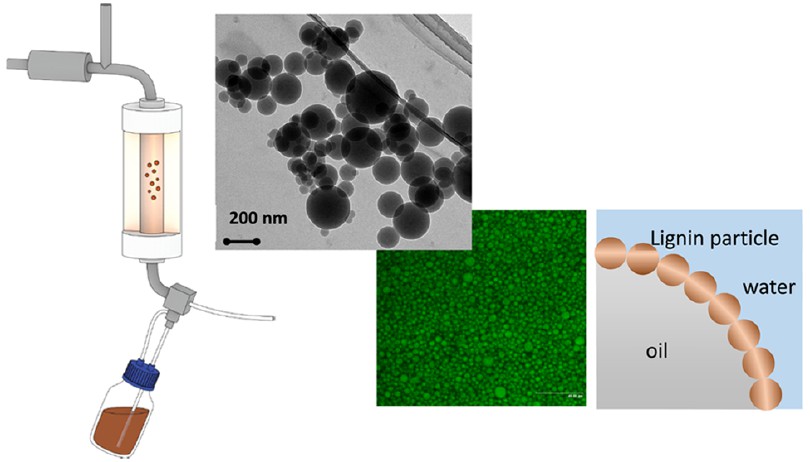
Preparation of lignin particles from aerosol flow reactor and their use in stabilization of Pickering emulsions (Ref.4)
Selected References:
1) Cusola O., Roncero M.B., Vidal T., Rojas O.J., Lignin particles for multifunctional membranes, anti-oxidative microfiltration, patterning and 3D structuring, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11, 45226-45236.
2) Cusola, O., Kivistö S., Vierros S., Batys P., Ago M., Tardy B.L., Greca L.G., Roncero M.B., Sammalkorpi M., Rojas O.J., Particulate coatings via evaporation-induced self-assembly of polydisperse colloidal lignin on solid interfaces, Langmuir, 2018, 34, 5759-5771.
3) Li S., Xie W., Wilt M., Willoughby J.A., Rojas O.J., Thermally stable and tough coatings and films using vinyl silylated lignin, ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6, 1988-1998.
4) Ago M., Huan S.Q., Borghei M., Raula J., Kauppinen E.I., Rojas O.J., High-throughput synthesis of lignin particles (similar to ~30 nm to similar to ~2 µu) via aerosol flow reactor: Size fractionation and utilization in Pickering emulsions, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8, 23302-23310.